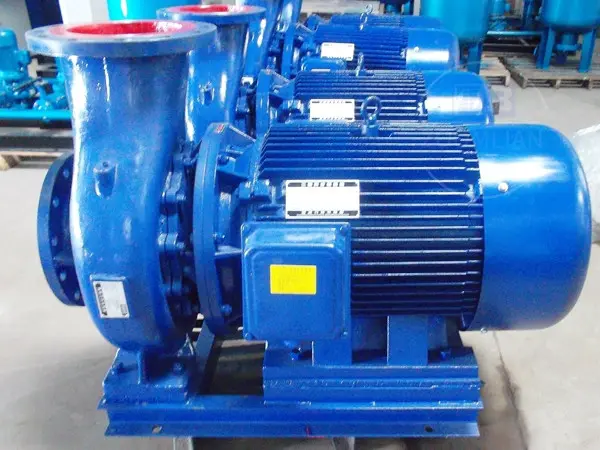
The MDEA natural gas decarbonization pump, also known as the lean solvent pump or amine water pump, uses MDEA, which stands for N-methyldiethanolamine. The MDEA decarbonization unit is a process designed to remove acidic gases from natural gas with high carbon dioxide content. In this process, the activated MDEA aqueous solution efficiently absorbs CO2 from high-pressure, ambient-temperature natural gas or syngas. Subsequently, by reducing pressure and increasing temperature, the absorbed CO2 is released back into the atmosphere, effectively regenerating the solvent. Since dissolved CO2 forms carbonic acid in water, which can increase the acidity of the liquid and lead to corrosion of steel, untreated natural gas could react with residual moisture in residential gas pipelines, forming carbonic acid that gradually erodes the pipeline walls, potentially causing leaks and even accidents. To ensure efficient purification and decarbonization, the MDEA amine-based decarbonization system relies on multi-stage decarbonization pumps. These pumps are not only ideal equipment for specialized CO2 removal tasks during raw gas purification in the synthetic ammonia industry but also serve as an outstanding choice for various other chemical processing applications.

Sinopec MDEA Natural Gas Decarbonization Pump: Models, Parameters, and Structure
The DF-type corrosion-resistant multistage natural gas decarbonization pump is a single-suction, multistage, sectional-style corrosion-resistant chemical centrifugal pump. It adopts a highly efficient and energy-saving national hydraulic model, offering excellent corrosion resistance and zero leakage. The flow-through components are available in either cast steel or cast stainless steel, with the material selection determined by the temperature and corrosiveness of the conveyed medium. The shaft features a fully enclosed design, ensuring it remains completely isolated from the process fluid, thus preventing corrosion and guaranteeing an exceptionally long service life. This pump is primarily used in industries such as petroleum, chemical processing, synthetic fibers, fertilizer production, power plants, metallurgy, food processing, and pharmaceuticals—enabling the reliable transfer of corrosive liquids ranging from -20°C to 105°C, as well as low- or high-temperature fluids, whether neutral or chemically aggressive. Many customers in the petrochemical sector specifically choose this pump for its role as a high-pressure decarbonization amine liquid circulation pump.

↑Click the image to learn more about the DF-type corrosion-resistant multi-stage natural gas decarbonization pump—view product details and parameter information↑
Main parameters of the DF-type natural gas decarbonization pump
Flow rate: 3.7–1350 m³/h Head: 49–1800 m Efficiency: 32%–84%
Pump weight: 78–3,750 kg Motor power: 3–1,120 kW NPSH required: 2.0–7.0 m
Structural Features of the DF-Type High-Pressure Amine Solution Decarbonization Circulation Pump
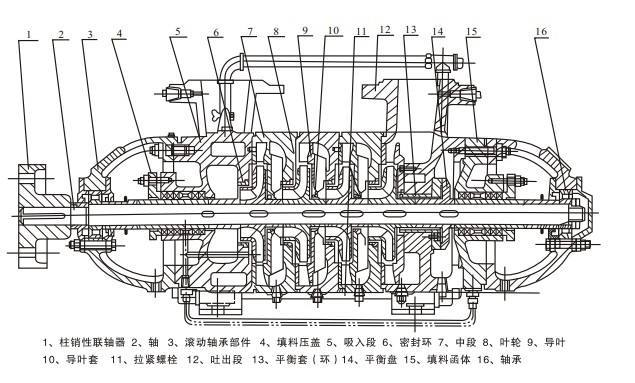
The inlet and outlet of the DF-type MDEA solution pump are both oriented vertically upward. The pump's suction section, middle section, and discharge section are securely connected as a single unit using tension bolts. The pump rotor consists of components such as impellers and balance discs mounted directly onto the shaft. At both ends of the rotor, rolling-element bearings or sliding bearings provide support; the rolling bearings are lubricated with grease. Axial forces acting on the rotor are counterbalanced by the balance disc.
1. Stator Section: Primarily composed of the suction section, middle section, discharge section, and guide vanes, these components are tightly secured together using tie rods to form the working chamber. The discharge outlet is oriented vertically upward, while the suction inlet is typically horizontal; however, depending on specific requirements, the system can also be manufactured with both inlet and outlet positioned vertically upward.
2. Rotor Assembly: Primarily composed of components such as the shaft, impeller, balance disc, and sleeve. The shaft transmits power to the impeller, enabling it to operate; the balance disc is used to counterbalance axial forces; and the shaft is fitted with a replaceable sleeve to protect the shaft itself.
3. Bearing Section: Primarily composed of the bearing housing, bearings, and bearing press covers, among other components. With the exception of pumps型号 85-67, 155-67, and 600-60, which utilize sliding bearings with dilute oil lubrication, all other pump models are equipped with rolling bearings lubricated by grease. Notably, pumps型号 85-67 and 155-67 can also be configured with rolling bearings.
4. Shaft Seal: Typically, a soft packing seal is used, consisting mainly of the sealing gland housing mounted on the suction section and tail cover, along with packing material and water-blocking rings. The sealing chamber is supplied with water at a certain pressure, serving functions such as water sealing, water cooling, and lubrication. For D-type MDEA solution pumps, the water seal typically relies on high-pressure water from within the pump itself, either directly sourced from the pump’s internal pressurized water or supplied externally. In contrast, DF-type pumps more commonly employ mechanical seals.
Transmission: The pump is directly driven by the prime mover via an elastic coupling. When viewed from the side of the prime mover, the pump rotates clockwise.
Sinopec MDEA Self-Balancing Natural Gas Decarbonization Pump
The MDEA self-balancing natural gas decarbonization pump innovatively reimagines the structure of traditional multistage centrifugal pumps, eliminating Conventional Multistage Pump The axial force balancing device, which utilizes a symmetrically arranged Impeller The rotor components' opposing forces counterbalance the axial force, effectively eliminating axial movement. This design prevents efficiency losses caused by disc friction and backflow in the balance disc during operation, resulting in an efficiency improvement of 3–12% compared to conventional multistage pumps of the same type. Additionally, it completely addresses various failures—such as wear on the balance disc and its seat, or even rotor seizure—that often occur when the balancing mechanism fails, significantly extending the pump's service life. Years of user feedback have consistently demonstrated that our company's self-balancing multistage pumps outperform competing models. Traditional Multi-stage Pump Reliability and efficiency have been significantly improved, with trouble-free operating time increasing by more than threefold, effectively extending the service life. This not only directly helps users save on production costs but also substantially reduces operational and maintenance expenses.
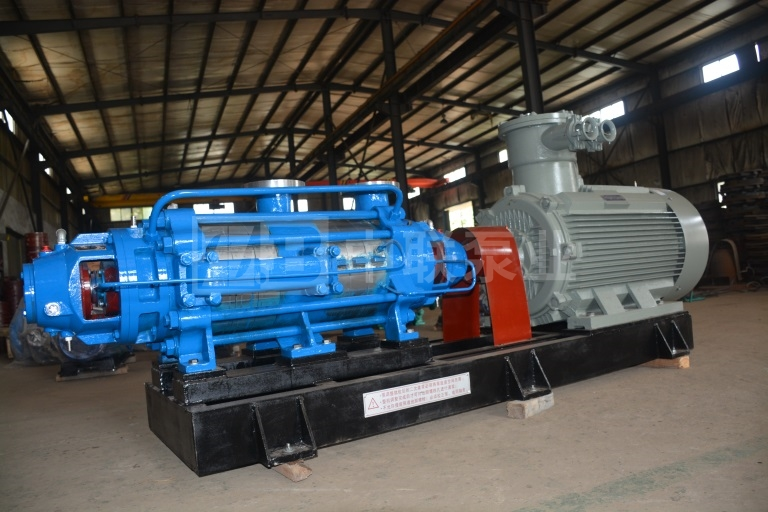

↑Click the image to learn more about the self-balancing natural gas decarbonization pump—view product details and parameter information↑
The MDEA self-balancing natural gas decarbonization pump is designed for transporting corrosive liquids free of solid particles, with temperatures ranging from -20°C to 105°C. Users can rationally select the pump material, sealing configuration, pump design, and determine the motor power based on factors such as the name, concentration, specific gravity, operating temperature, and inlet pressure of the conveyed medium.
Previous:
Recommended Information
Related Products















