A self-balancing, multi-stage pump featuring either single-suction or double-suction inlet designs in its first-stage impeller—this horizontal sectional, multi-stage, self-balancing centrifugal pump has been newly developed by our Changsha Zoomlion Pump Industry company. Drawing on advanced technologies from similar foreign products, we’ve seamlessly integrated these innovations with our own decades of expertise in pump R&D. Designed to meet the diverse needs of pump users and drive further advancements in the pump industry, this model was meticulously crafted according to the API1601 standard, making it a reliable replacement for conventional pumps. Type D Multistage Centrifugal Pump High-efficiency and energy-saving products. They feature a wide efficient operating range, extensive performance capabilities, excellent cavitation resistance, fewer wear parts, and convenient installation and maintenance.

The self-balancing multistage centrifugal pump features a high-pressure-resistant, high-performance hydraulic design, innovatively reimagining the traditional multistage centrifugal pump structure by eliminating the conventional axial force balancing mechanism. As a result, its operational efficiency is more than three times higher than that of standard multistage pumps, significantly boosting users' economic benefits while dramatically reducing production costs. This pump serves as an excellent alternative to D- and DG-type multistage centrifugal pumps that typically rely on balance disc or balance drum designs. Moreover, since this pump is equipped with no balancing device—meaning there’s neither disc friction loss from the balance disc nor recirculation losses associated with the balance mechanism—it achieves a 5% to 14% improvement in pump efficiency compared to similar multistage pumps. At the same time, it completely resolves various issues caused by the failure of traditional balancing systems, such as wear on the balance disc and its seat, or even rotor seizure, thereby substantially extending the pump’s service life.
Self-balanced Multistage Centrifugal Pump Structural Diagram:
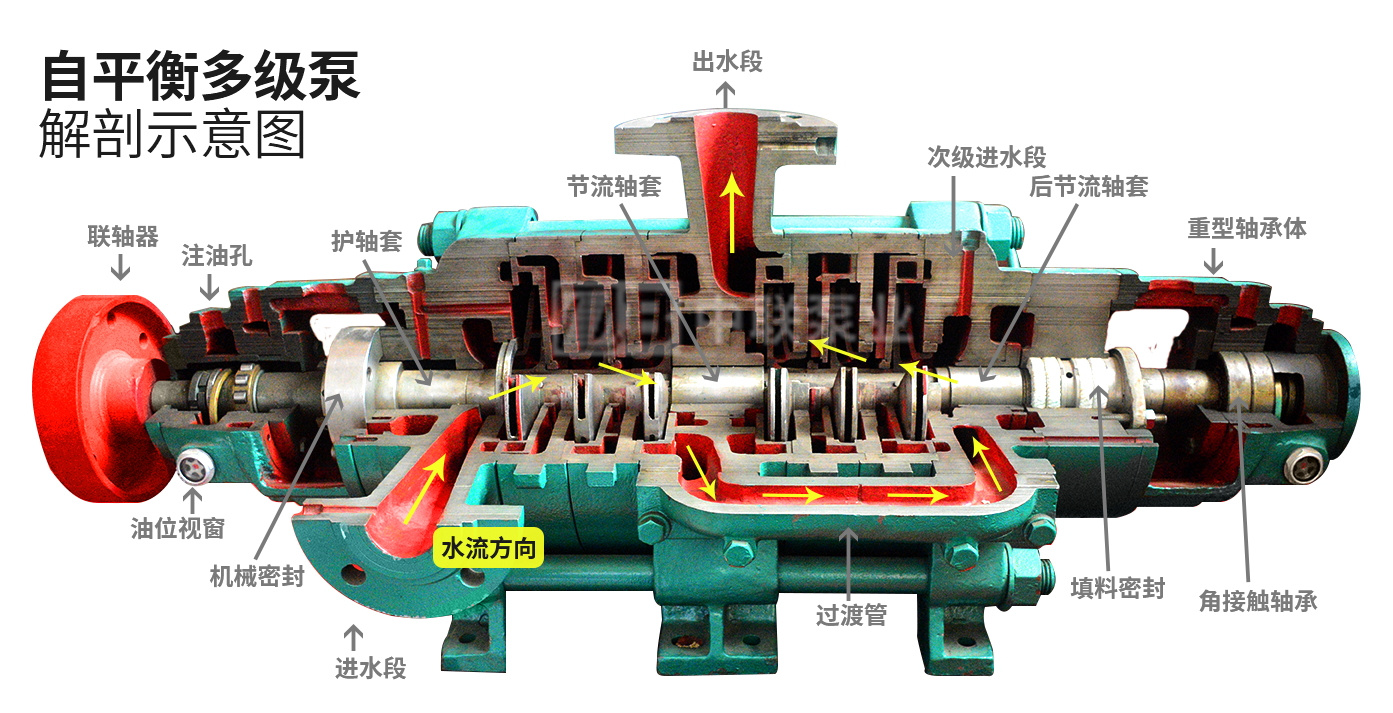
Anatomical Diagram of a Self-Balanced Multistage Pump Structure
The self-balancing multistage centrifugal pump's shaft rotates driven by the motor, doing work on the liquid and increasing its energy. As a result, the required amount of liquid is continuously delivered—first drawn from the suction sump, then passing through the pump's inlet section, forward impeller, forward guide vanes, middle section, horizontal discharge outlet in the discharge section, transition pipe, secondary inlet section, reverse impeller, reverse guide vanes, and finally exiting via the vertical discharge outlet in the discharge section.
Self-balanced multistage centrifugal pump structural diagram:
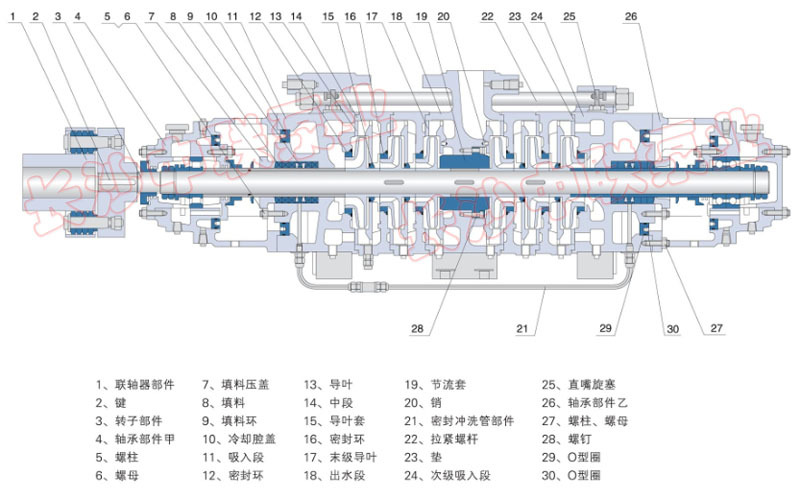
Self-Balanced Multistage Pump Structural Diagram
● The self-balancing multistage pump is a sectional, single-suction (or double-suction at the first-stage impeller) centrifugal pump designed for self-balancing. Its suction inlet can be arranged vertically upward or horizontally, while the discharge outlet is positioned vertically upward. The pump primarily consists of components such as the suction section, middle section, discharge section, secondary suction section, forward guide vanes, reverse guide vanes, forward impeller, reverse impeller, shaft, throttling and pressure-reducing device, sleeve, bearing housing, transition pipe, and more. The middle section is securely connected to the suction and discharge sections via high-strength through-bolts. Additionally, the sealing surfaces between the suction, middle, and discharge sections are equipped with aluminum-based lubricant for robust metal-to-metal hard sealing. The rotor assembly includes the forward impeller mounted on the shaft, along with the throttling and pressure-reducing device, reverse impeller sleeve, and bearing sleeves. The bearings feature a "fixed-floating" dry-lubrication design: the drive end uses cylindrical roller bearings, while the tail end employs angular-contact ball bearings. The pump's working chamber comprises the suction section, middle section, discharge section, secondary suction section, forward guide vanes, reverse guide vanes, transition pipe, and other key components.
● The rotor section is sealed against the stationary part using components such as sealing rings and guide vane sleeves. When wear on the sealing rings and guide vane sleeves begins to affect the pump's performance, they should be replaced promptly.
● The pump features two types of shaft seals: mechanical seals and packing seals. When the pump is equipped with a packing seal, the packing rings must be positioned correctly, and the tightness of the packing material should be adjusted appropriately—ideally allowing liquid to seep out drop by drop. All sealing components of the pump are housed within a sealed cavity, which is continuously supplied with water at a specific pressure. This water serves multiple functions: providing a water seal, cooling the system, and offering lubrication. Additionally, a replaceable shaft sleeve is installed at the shaft seal area to protect the pump shaft. As a result, bearings and seals can be replaced without needing to disassemble the inlet and outlet pipelines.
● The self-balancing multistage centrifugal pump is directly driven by the prime mover via an elastic pin coupling or a diaphragm coupling. When viewed from the direction of the prime mover, the pump rotates clockwise.
● The motors are typically configured with the Y3 series; in environments with combustible and explosive gases, the YB3 series explosion-proof motors are used.
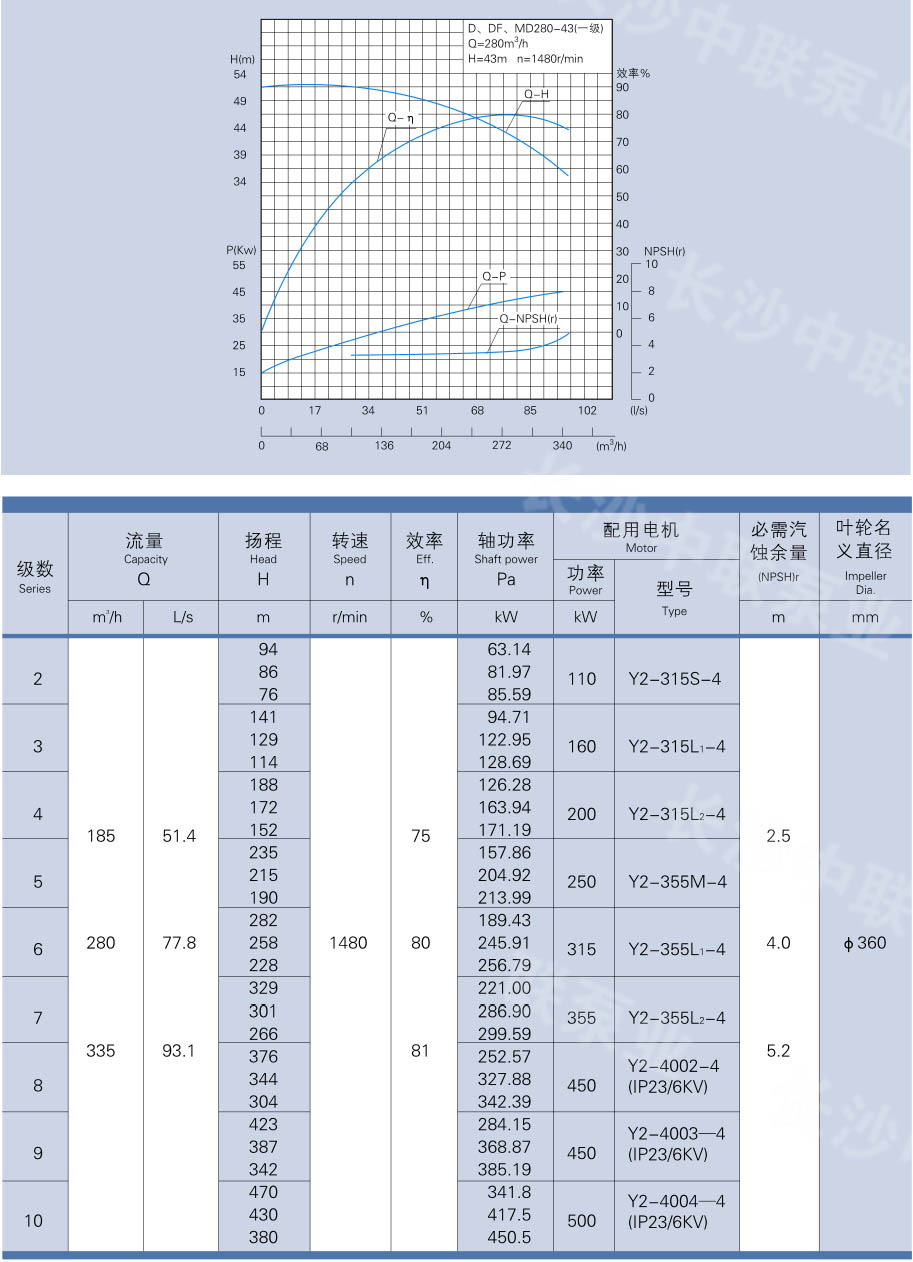
Performance parameters and curve examples for self-balancing multistage pumps:
Previous:
Recommended Information
Related Products















